
Start dates
Fall (Sept), Winter (Jan)
Program length
48 months, 120 credits
Majors
NA
Program Delivery
On-campus
Shape the future of animal care
Prepare for a future in veterinary medicine or advanced research with an Honours Bachelor of Science in Bioveterinary Science. Combining foundational biological sciences with cutting-edge digital technologies, you’ll gain a deep understanding of animal health and welfare.
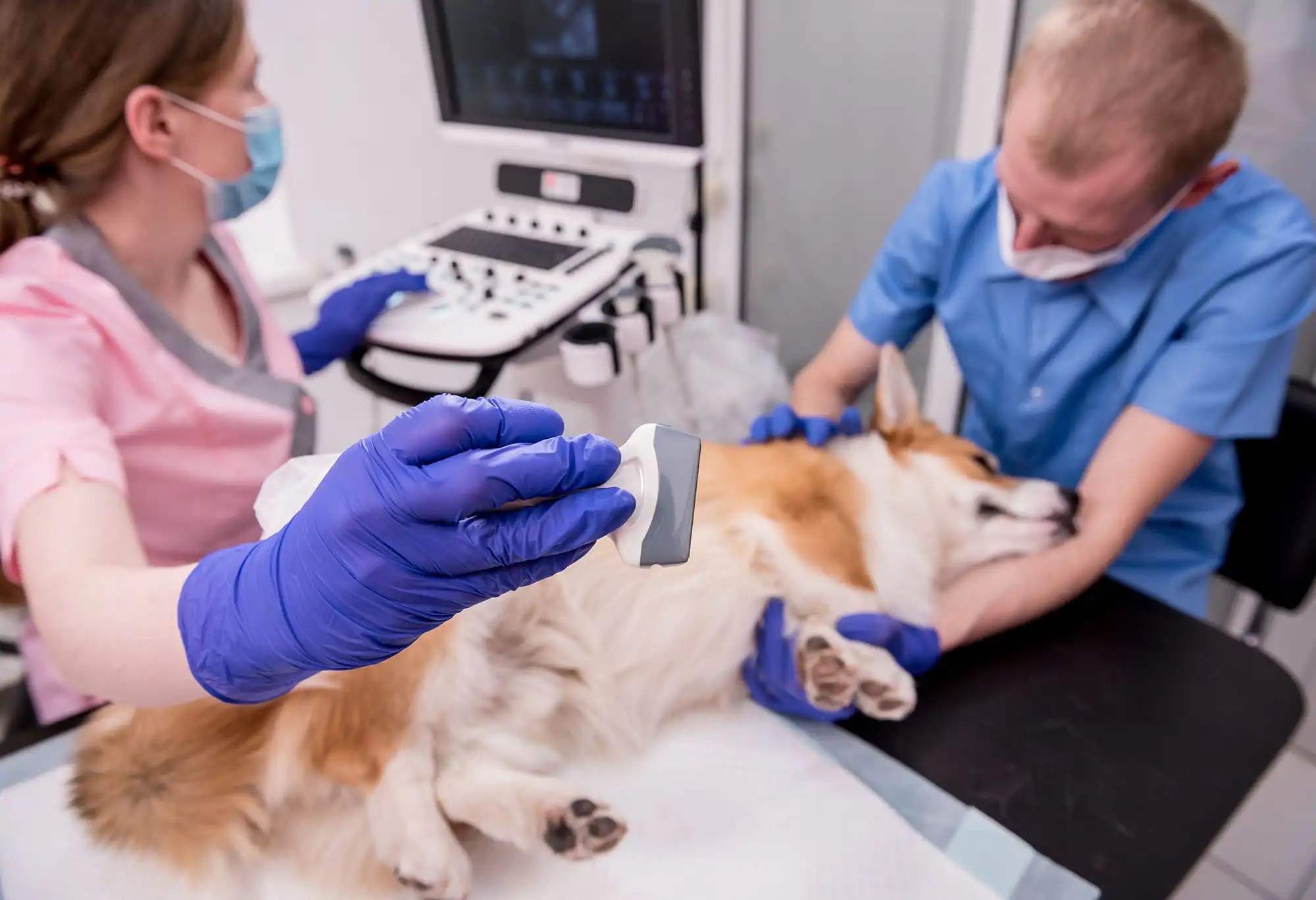
Course highlights
Term 1
Term 2
Term 3
Term 1
Term 2
Term 3
Term 1
Term 2
Term 3
Term 1
Term 2
Term 3
These course highlights provide a glimpse into the Honours Bachelor of Science in Bioveterinary Science program, your actual schedule may vary. There is a program break during Term 4 each year. For full course descriptions and schedules, consult the Academic Calendar.
Admission requirements for the Honours Bachelor of Science in Bioveterinary Science

Academic information
Applicants must meet the following minimum conditions for admission:
- Ontario Secondary School Diploma (or equivalent credential)
- Six Grade 12 4U or 4M-level course, including Ontario ENG4U (or equivalent) and any 1 4U Math
- Minimum average of 70% on best 6 Grade 12 4U or 4M-level courses
- Must meet English language proficiency requirements (if applicable)
Document checklist
Applicants must submit:
- A completed application form
- Official transcripts from all post- secondary institutions attended
- Official documentation confirming professional designations, where applicable
- Proof of English language proficiency, if applicable
International information
Applicants who completed undergraduate studies outside Canada must also submit:
- Certified translations of any documents not in English
- Documentation confirming award of their previous degree(s), if not already indicated on official transcripts
- A credential evaluation from a recognized service, if required by the registrar
Tuition information
Choosing to pursue a university education is a big commitment that impacts every aspect of your life – including your finances. Our fees are determined by the total cost of individual credits per academic year. All fees are listed in Canadian dollars and these rates are subject to change.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
The Office of the Registrar had dedicated more than $15 million in scholarships, awards and financial support to students in 2026. Entrance Awards are for newly admitted international and domestic students, while Academic Scholarships are for those entering the second term of their program.
Career highlights
With a strong foundation in biological sciences, the BSc Bioveterinary Sciences program prepares you for a career at the forefront of animal care.
Veterinary
Scientific
Technical
Government
Career paths after graduating with a Honours Bachelor of Science in Bioveterinary Science
There is a growing demand for veterinary professionals in Canada, leading to notable workforce shortages.
Between 2022 and 2031, approximately 5,000 job openings for veterinarians are anticipated, while only about 4,300 new job seekers are expected to be available, indicating a projected shortage in the field.
Career path and salary
- Veterinarian (after additional education) - $107,731
- Wildlife biologist - $87,301
- Animal ecologist - $100,000
- Animal nutrition specialist - $83,200
- Wildlife conservation - $80,181
*Source, Talent.com

Frequently asked questions
What are some of the unique features of the BSc Bioveterinary Science program?
It integrates digital technologies like VR and AI into the curriculum and there are virtual lab components, aligning with animal welfare principles. There is an emphasis on teamwork and communication through group-based learning activities.
How does the program prepare students for veterinary school?
The curriculum provides a strong foundation in biological sciences relevant to veterinary medicine, along with courses like animal behavior and veterinary professional development. The program also fosters research and critical thinking skills valued by veterinary schools.
What are core electives?
Core electives will build on some of the more specialised areas of the program and will give you the ability to streamline your program. A minimum of three core electives must be selected: Animal Behaviour, Animal Welfare, Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy, Parasitology, Introduction to Epidemiology, Veterinary Professional Development.
What are non-core breadth electives?
The non-core breadth electives are divided into three groups: Social Sciences and Humanities, Sciences and Mathematics, Global Cultures (including Indigenous cultures). You must choose non-core breadth elective courses from at least two of the three groups.
What are the learning outcomes of this program?
The program focuses on developing a strong foundation in biological and biochemical sciences, chemical and physical foundations of biological systems, scientific inquiry and reasoning, communication skills (written and visual), digital literacy, and foundational understanding of animal behaviour.
Is Bioveterinary Science a good degree?
Yes, an HBSc Biovet degree offers a strong foundation in animal-health sciences, combining general science like biology, chemistry, anatomy, and physiology, with specialized courses in animal health, welfare, and veterinary-related topics.
What can you do with a Bioveterinary Science degree?
It prepares students for further veterinary education or graduate study in animal and biological sciences. It also helps to connect graduates to a number of meaningful careers including animal nutrition specialist, wildlife conservation officer or biologist, food inspection or food-safety roles – especially in animal products, animal behaviour or animal welfare technician, research assistant or technician in animal and Bioveterinary science, and technical roles in animal agriculture.
What is the highest paying veterinary specialty?
The highest paying veterinary-related degree in Canada tends to be a DVM (Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) plus specialization. For example, specialists in surgery, critical care, etc. Veterinarians who specialize can earn significantly more than general practitioners. The exact figures and demand can vary based on location, type of practice, and hours.
Talk to a Student Advisor
This institution has been granted a consent by the Minister of Colleges and Universities to offer this program for a five-year term starting Dec. 10, 2025. Prospective students are responsible for satisfying themselves that the program and the degree will be appropriate to their needs (e.g., acceptable to potential employers, professional licensing bodies or other educational institutions.)